
HTML101:
Intro to HTML & CSS
Welcome!
Some "rules"
- We are here for you!
- We love your questions
- Help each other
- Try to avoid:
- Feigning surprise
- Well-actually's
- Have fun
Tell us about yourself.
- Who are you?
- What do you hope to take home from this class?
- What is your favorite thing to do when you have some free time?
Get Started: Folder Structure
All the files for your site should be stored within the same folder.
This includes:
- HTML Files
- CSS Files
- Images
- Script files
- Anything else that will appear on your site
Note: File names should not include spaces or special characters. File names ARE case sensitive.

What is HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
is the code that allows us to build websites
Why use HTML?
The web is mostly used for 2 things:
Basic HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Why New Elements - HTML5?
- SEO & Search Engines
- Web Accessibility
- Code is for humans too
Attributes & Values
-
Attribute
- Class, id, language, style, identity, source
- Allows you to add more info to the element
- Placed inside an opening tag, before the right angle bracket.
-
Value
- Value is the value assigned to a given attribute.
- Values must be contained inside quotation marks.
<img src="my_picture.jpg" />
<a href="http://girldevelopit.com">GDI</a>
<section id="copyright">© GDI 2013</section>
<section class="important">Remember!</section>
Element: Link
Links have three components
- Tag: <a></a>
- Href attribute: "http://www.girldevelopit.com"
- Title attribute: "Girl Develop It"
<a href="http://www.girldevelopit.com" title="Girl Develop It Homepage">GDI</a>
The <a> tag surrounds text or images to turn them into links
Link Attributes
Links can have attributes that tell the link to do different actions like open in a new tab, or launch your e-mail program.
<a href="http://bit.ly/NDTPQJ" target="_blank">GDI SLC Meetup</a>
Link opens in a new window/tab with target="_blank"
<a href="mailto:saltlakecity@girldevelopit.com">E-mail us!</a>
Link opens mail program by inserting mailto: directly before the email address.
CSS: What is it?
CSS = Cascading Style Sheets
CSS is a "style sheet language" that lets you style the elements on your page.
CSS is works in conjunction with HTML, but is not HTML itself.
The CSS Rule
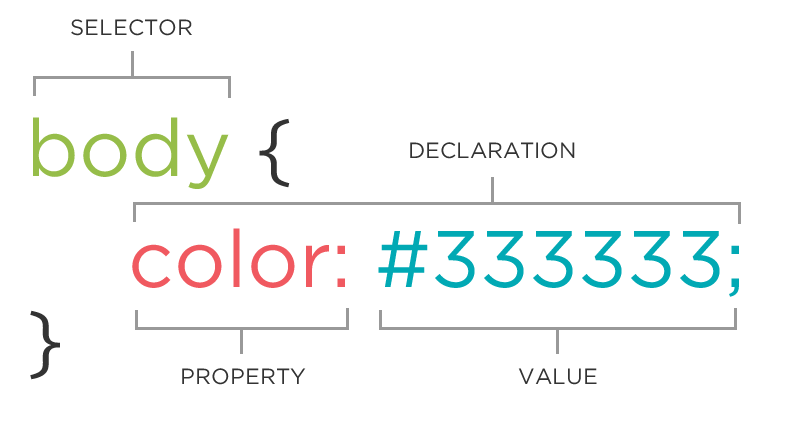
Connecting CSS to HTML
3 ways
"External"
"Embedded"
"Inline"
Connecting CSS to HTML: External/Linked
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
Shared resource for several pages.
Reduced file size & bandwidth
Easy to maintain in larger projects.
Preferred by coders everywhere!
Connecting CSS to HTML: Embedded
<head>
<style type="text/css">
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
</style>
</head>
Inside <head> element.
Uses <style> tag.
Can only be used in one html file
Connecting CSS to HTML: Inline
<p style="color:red;">Some text.</p>
Uses the HTML attribute style.
Difficult to use in large projects
Not preferred.
Border
The edge around the box, specified as "thickness, style, color."
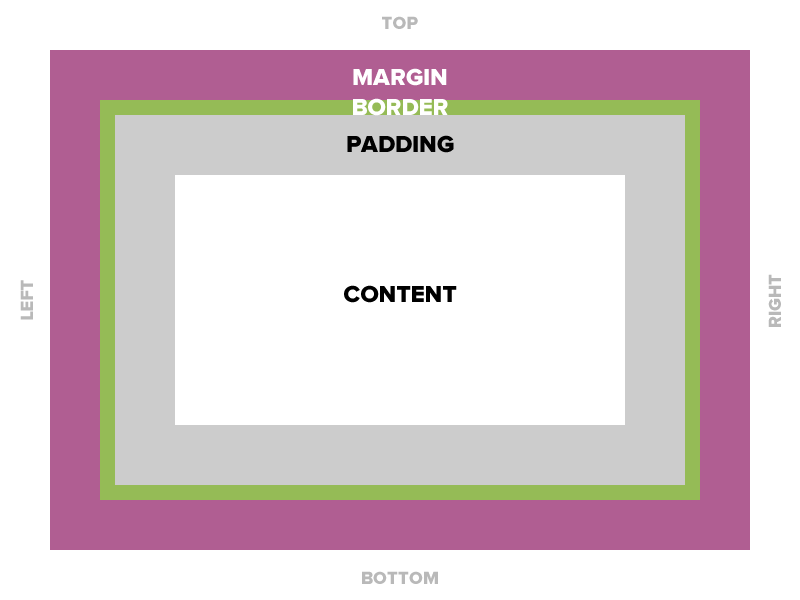
Border
A solid red border
border: 1px solid #ff0000;
A thick dotted black top border
border-top: 4px dotted #000000;
Two different border styles
border-top: 1px solid #ff0000;
border-bottom: 4px dotted #000000;
Property: Width
Sets the width of an element.
Does not include padding or borders. These add to the width.
body {
width: 900px;
}
Property: Height
Sets the height of an element.
Does not include padding or borders. These add to the height.
body {
height: 900px;
}
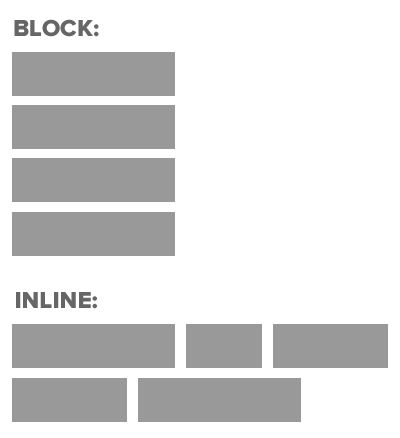
Inline vs Block
So far, we have mostly seen "block" elements. They appear on the next line, like paragraphs
<p>, <h1>, <ul>, <li>, almost everything else
There are also "inline" elements. They appear on the same line that they are written on.
Float: Example
"Floating" an element moves it, in the normal flow, as far to the left or right of its parent element as possible.

Above a <blockquote> is floated to the left, allowing text to wrap around it on the right
Float: Wrapping
Any other elements, such as paragraphs or lists, will wrap around the floated element.
.float{
float:left;
width:200px;
background:yellow;
}
I like to hang out on the left side.
Using floats to place elements side by side
If you want two block level elements to be side by side, you need to float both elements. One left, and one right.

Always specify a width when floating an element, otherwise the element is likely to take up the whole page and not appear floated.
Alternates to Float
Clear
- Tells the element on which side (right, left, both) other elements cannot appear.
- Clearing both sides makes sure floats don’t flow past the clear element.
clear: right;
clear: left;
clear: both;
Clear
If you had an image, div, etc. floated left, and you did not want the paragraph to appear next to it, you would add clear: left; to the paragraph.
.float{
float:left;
width:50px;
background:yellow;
}
.clear-left{
clear:left
}
hi
hi
Font-family
The font-family property defines which font is used.
p {
font-family: "Times New Roman";
font-family: serif;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
Specific font name
Generic name
Comma-separated list
Only have to use quotation marks ("") when the name has spaces
Property: Font-size
The font-size property specifies the size of the font.
p {
font-size: 12px;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-size: 100%;
}
Pixels
"rem" or "em"
Percentage
Fonts (shorthand)
p {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 10px;
font-family: sans-serif;
}
OR
p {
font: italic bold 10px sans-serif;
}
Padding
Space between the border and the content
Adds to the total width of the box.
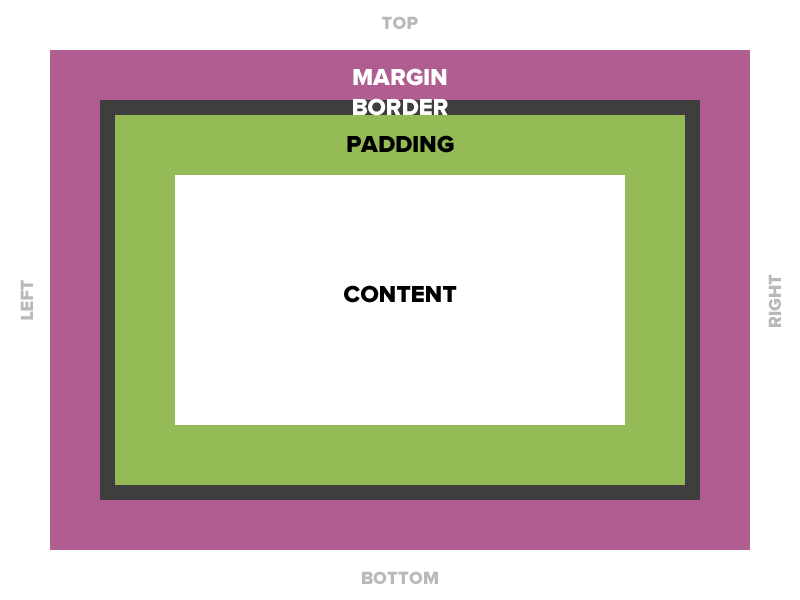
Padding
20 pixels* on top only
padding-top: 20px;
20 pixels on right only
padding-right: 20px;
20 pixels on bottom only
padding-bottom: 20px;
20 pixels on left only
padding-left: 20px;
*Like font-size, you can also use em, rem, or percentages
Padding
15 pixels on all sides
padding: 15px; /* All sides */
20 on top, 15 on right, 13 on bottom, 25 on left
padding: 20px 15px 13px 25px; /* Top, Right, Bottom, Left */
10 on top/bottom, 45 on right/left
padding: 10px 45px; /* Top/Bottom Right/Left */
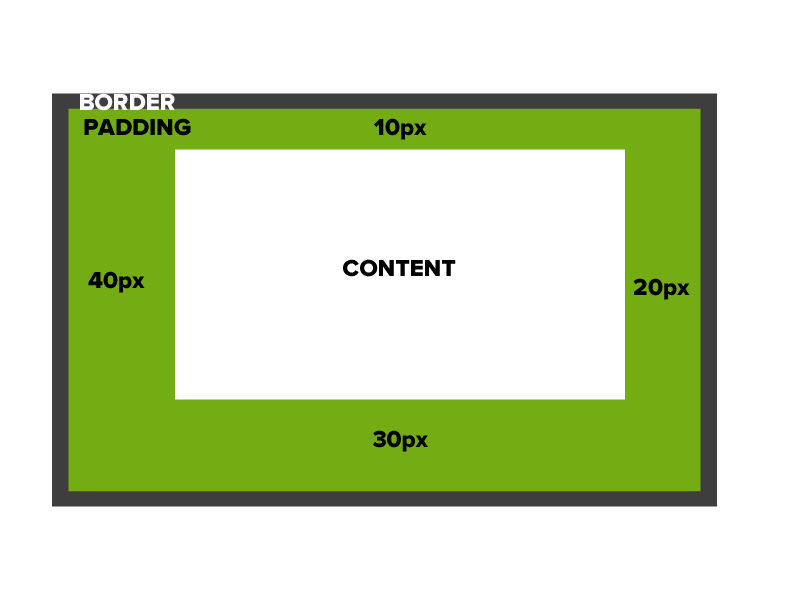
Padding
padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
Margin
The transparent area around the box that separates it from other elements.

Margin
One side
margin-top: 10px; /* 10 pixels on top */
All sides
margin: 15px; /* 15 pixels on all sides */
Top, Right, Bottom, Left
margin: 10px 5px 3px 5px; /* 10 on top, 5 on right, 3 on bottom, 5 on left */
Top/Bottom, Right/Left
margin: 10px 20px; /* 10 on top/bottom, 20 on right/left */
Auto Margin
If a margin is set to auto on a box that has width, it will take up as much space as possible.
CENTERED
margin: auto;
width: 300px;
FLUSH-RIGHT
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: 5px;
width: 300px;
Text-Align
Aligned left (default)
text-align: left;
Aligned right
text-align: right;
Aligned center
text-align: center;
Justifying all of the text
text-align: justify;
Line-Height
Unitless (multiply this number by the font-size)
line-height: 1.5;
Using rem or em's
line-height: 1.5em;
Using percentages
line-height: 150%;
Span
Span is used to apply a specific style inline
.yellow {
color: yellow;
}
<p>Paragraph with <span class ="yellow">yellow</span> text.</p>
Paragraph with yellow text.
Color
The color property changes the color of the text.
p {
color: red; /* Color name */
color: #ff0000; /* Hexadecimal value */
color: rgb(255, 0, 0); /* RGB value */
}
The 17 standard colors are: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, grey, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, and yellow.
Background-color
The background-color property changes the color of the background.
p {
background-color: black;
background-color: #000000;
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
}
Pseudo-classes (links)
CSS pseudo-classes are used to add additional functionality to some selectors.
a:link { color:#FF0000; } /* unvisited link */
a:visited { color:#00FF00; } /* visited link */
a:hover { color:#FF00FF; } /* mouse over link */
a:active { color:#0000FF; } /* selected link */
Note: a:hover MUST come after a:link and a:visited in order to be effective!
Note: a:active MUST come after a:hover in order to be effective!
Text-Decoration
Underlined
text-decoration: underline;
Overline
text-decoration: overline;
Line through your text
text-decoration: line-through;
Shorthand*
text-decoration: underline wavy red;
Div
Div is a block level element. Each new div is rendered on a new line. It has no semantic meaning.
Used to group elements to format them with CSS.
<div>
<p>Content<p>
<p>Content<p>
</div>
<div id="header-group">
<header>
<h1>Main Heading<h1>
</header>
<nav>
<ul><li>Home</li></ul>
</nav>
</div>
Apply IDs and Classes to divs to control their styles with CSS.
Relative vs. Absolute paths
-
Relative
- Relative paths change depending upon the page the link is on.
- Links within the same directory need no path information. "filename.jpg"
- Subdirectories are listed without preceding slashes. "images/filename.jpg"
- Relative paths change depending upon the page the link is on.
-
Absolute
- Absolute paths refer to a specific location of a file, including the domain. "http://www.girldevelopit.com/chapters/detroit"
- Typically used when pointing to a link that is not within your own domain.
Website Examples
Questions? Contact Me
Email: stacie@girldevelopit.com
Twitter: @FarmerCode
What Next?
Refreshers
Learning HTML for Kids (and Adults)
Study Errors Beginners Make While Learning HTML & CSS